Passive optical local area networks, or POLs, are wireless networks that don’t use electrical power. This type of network also does not emit heat, so it can reduce energy costs and help reduce environmental impact. This type of network does not require telecom rooms or wiring closets, and is therefore easier to build and design. Additionally, it doesn’t require cooling, making it a greener option than copper cable.
Passive optical networks offer a variety of benefits, including a long lifecycle and a low cost of ownership.
VoIP providers also used passive optical local area networks. They also consume considerably less energy, making them a preferred choice for businesses and homeowners alike. Because they reduce energy usage, they have also become increasingly popular among formal bodies and government agencies.
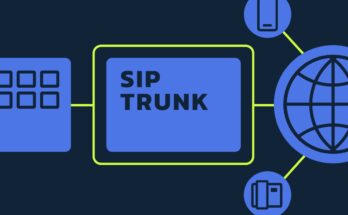
The two major components of a PON are an OLT and an ONU. The OLT is the service provider’s end of a PON network and is responsible for converting electrical signals into fibre optic signals. On the other hand, the ONU is located at the customer’s end of the network. The ONU combines the incoming optical signals with data signals.
The passive optical local area network market is segmented by component, type, application, and end user. This report examines the global passive optical local area network market by country. Using a country-by-country analysis, it shows the growth of this technology and identifies key drivers and barriers. Passive optical local area networks are a great option for companies seeking reliable and secure networks.
Passive optical local area networks, also known as PON, are a great way to lower your capital costs. The fiber optic cable in PON is used in buildings with high bandwidth demands, such as offices, hotels, libraries, and chains of nursing homes. The PON technology was initially used in government agencies, but the technology was quickly adopted and installed in offices and other large businesses.
In October 2013, major companies launched gigabit and Ethernet passive optical networks. Despite the rapid growth of the passive optical network, it is still a relatively new technology. However, key players are focused on research and development. As of October 2013, Alcatel-Lucent has launched a complete EPON solution based on its highest-capacity fiber platform.
The first versions of PON technology came to market in the 1990s. Since then, PON technology has advanced a lot. Many of the standards that were used then have been replaced by newer versions. This has made the technology more secure than other types of networks. If you’re interested in implementing this technology, you need to know how it works.