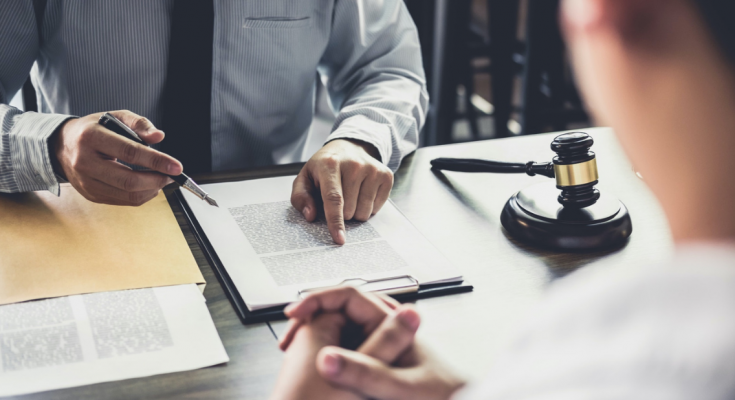
Do you disagree with the reason for your dismissal? Do you think you were fired without real and serious cause? Dismissal is precisely regulated by the Labor Code an employer cannot arbitrarily terminate an employee’s employment contract. If your employer has dismissed you on the basis of non-existent or low-level grounds, you can initiate proceedings and obtain compensation. In this article we will guide you about what is wrongful termination and what to do and what compensation to expect?
Wrongful dismissal: what possible remedies?
The different remedies that can be awarded to the employee for unfair dismissal vary according to his seniority and the size of his company.
The reintegration of the employee into the company
If the employee has at least 2 years of seniority and his company includes at least 11 employees, the judge can propose the reinstatement of the employee in the company. The employee will then be able to keep all the advantages he had acquired. If the employee has less than 2 years of seniority and/or his company has less than 11 employees, the judge cannot propose the reinstatement of the employee.
Compensation for unfair dismissal
As soon as the employee or the employer refuses reinstatement in the company, the employee may be entitled to compensation for unfair dismissal at the expense of the employer. The amount of compensation for unfair dismissal is governed by the Labor Code.
As a result, the amount of compensation awarded by the judge must necessarily respect the legal scale of compensation for unfair dismissal. This scale sets minimum and maximum amounts of damages in months of salary. The amount of compensation for unfair dismissal varies according to the seniority of the employee and the number of employees in the company (more or less than 11 employees). To get an idea of the amount of your compensation, you can consult our sheet on the calculation of severance pay.
How to justify a dismissal.
To be likely to justify a dismissal, the insufficiency must be characterized over time: an employee can completely contest a dismissal for a lack of efficiency over a few days or a few weeks. It must also be consistent with the employment contract and working conditions. An employee can thus show that the shortcomings complained of correspond to missions which were not provided for in the employment contract, that the employer did not make him follow the appropriate training, did not give him the time and the means to adapt to his new position or gave him an excessively heavy workload. The employer must also have informed the employee of his errors or shortcomings so that he can improve: if no communication on this subject was carried out, it is an additional argument of defense for the employee. If one of these arguments is upheld by the judges, they may consider the dismissal to be without real and serious cause, and the employee may request his reinstatement.
It is also possible to attack the dismissal on the form. An employer who invokes a dismissal for fault when it is a simple insufficiency is thus at fault. Similarly, if he does not comply with the dismissal procedure for personal reasons, the dismissal may be considered irregular and give rise to the right to compensation.